What’s the difference between Leqembi and Aduhelm? A simple overview.
Last updated: 19 November 2024
You can legally access new medicines, even if they are not approved in your country.
Learn howSince 2021, the FDA has granted accelerated approval to two new Alzheimer's medicines. These medicines are the anti-amyloid therapies Leqembi (lecanemab) and Aduhelm (aducanumab). Both approvals came after almost 20 years without major breakthroughs in Alzheimer's treatment. Because of this, both drugs have received wide media attention.
Reception has been mixed, however. Maria Carrillo, the Chief Science Officer for the Alzheimer's Association, referred to the new drugs' approvals as "a milestone for people eligible for this treatment" [2]. At the same time, their approval process has been surrounded by controversy, especially in Aduhelm's case [1, 4].
As a patient, you're probably wondering what is the difference between Leqembi (lecanemab) and Aduhelm (aducanumab). In this article, we'll compare the two drugs on the way they work, their efficacy, as well as their cost and availability.
Leqembi vs Aduhelm: What are they used for?
Both medicines are treatments for early Alzheimer's disease. They are anti-amyloid therapies and target amyloid plaques in the brain.
According to their prescribing information, Leqembi and Aduhelm are intended for patients with mild cognitive impairment and with confirmed elevated beta-amyloid levels [5].
Leqembi vs Aduhelm: How do they work?
Similarities
Leqembi (lecanemab) and Aduhelm (aducanumab) are both monoclonal antibodies. They are designed to target the beta-amyloid plaques that build up in the brains of Alzheimer's patients. These plaques are believed to contribute to the cognitive decline and clinical decline seen in this disease.
Both medicines bind to and neutralize amyloid plaques, with the aim of slowing the progression of the disease. This is what makes Leqembi and Aduhelm fundamentally different from previous Alzheimer's treatments such as galantamine, rivastigmine, and donepezil. These previous treatments focus on alleviating symptoms of the disease. Leqembi and Aduhelm aim to change the course of the disease by targeting its root cause.
Differences
Leqembi and Aduhelm bind to different parts of the beta-amyloid protein. Aduhelm binds more strongly to larger, hardened amyloid plaques. Leqembi is reported to better target the smaller, soluble (and more toxic) form of amyloid protein [6].
How efficient are Leqembi and Aduhelm?
The efficacy of Leqembi(lecanemab) and Aduhelm(aducanumab) has been studied in clinical trials.
-
Leqembi clinical trial results
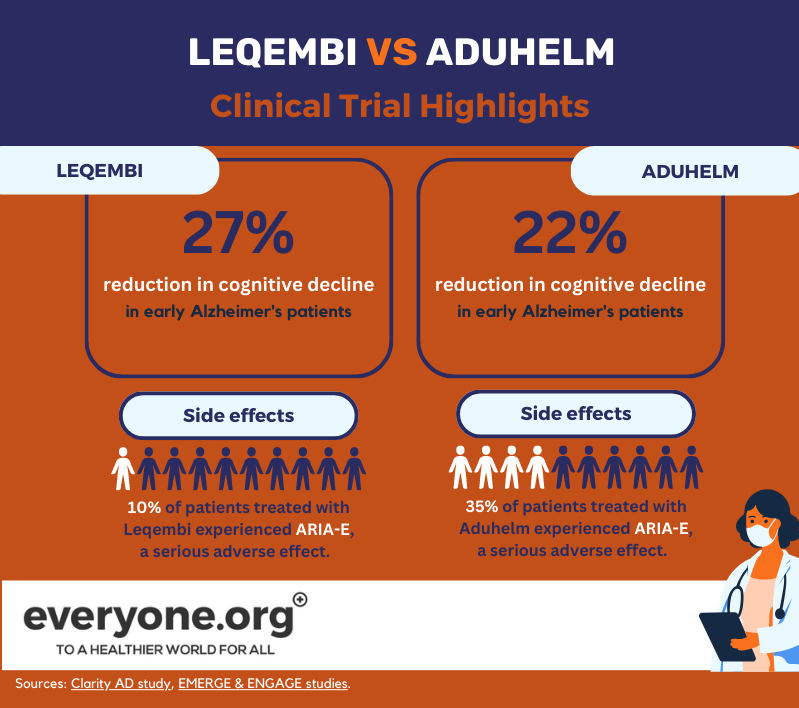
Leqembi's accelerated FDA approval was based on the positive top-line results from the Phase 3 Clarity AD study. According to these results, Lecanemab slowed cognitive decline of up to 27% in early Alzheimer's patients, compared to placebo. These results were measured at 18 months after starting the treatment [8].
An additional analysis of the study results was published in April 2023. It showed that even after patients stopped taking Leqembi for a period of 9 to 59 months, they still continued to benefit from a delay in cognitive decline. During this "gap period", Alzheimer's disease appeared to progress at a consistently slower rate in patients who received Leqembi in the original clinical trial, as compared to those receiving placebo [7].
The serious adverse effect of ARIA-E occurred in 10% of the patients treated with Leqembi. 6% of patients in the trial experienced ARIA-H, another serious adverse effect [13].
-
Aduhelm clinical trial results
The FDA granted its accelerated approval to Aduhelm on the basis of two Phase 3 clinical trials. One of them (EMERGE) showed a reduction in patients' clinical decline by up to 22% [12]. The other one (ENGAGE) didn't. In both studies, however, Aduhelm demonstrated a reduction in amyloid plaques in the brain [9]. The FDA decided that this indication is "reasonably likely to result in [a] clinical benefit" [10].
A Phase 4 confirmatory trial (ENVISION) started in June 2022, as per the FDA's request. Results are expected in 2026 [9].
According to Aduhelm's prescribing information, 35% of patients receiving the medicine in clinical trials experienced ARIA-E. 34% of trial patients experienced ARIA-H [15].
As these current data show, the main difference between Leqembi and Aduhelm at this point seems to be in their safety profile, with Leqembi showing a lower incidence of adverse effects.
At the same time, based on current clinical trial data, Leqembi appears to deliver a more consistent effect on cognitive decline. The results of ongoing trials on both Leqembi and Aduhelm will deliver more clarity on both medicines' performance.
NOTE: The results shared here are for informational purposes and should not be used as the basis of a treatment choice. Your doctor is in the best position to determine the treatment that best applies to your case.

Leqembi vs Aduhelm: Safety and side effects
According to their prescribing information, these are the most common side effects of Leqembi (lecanemab) and Aduhelm:
Leqembi side effects
- infusion-related reactions, including fever, flu-like symptoms, nausea, changes in hear rate, and shortness of breath;
- headache;
- Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities (ARIA) [13]. ARIA may involve temporary swelling or bleeding in the brain. Symptoms of ARIA are headaches, confusion, seizures, difficulty walking, and dizziness. Carriers of the homozygous apolipoprotein E gene may be at a higher risk of ARIA [14].
Aduhelm side effects
The most common side effects of Aduhelm are ARIA, headaches, and fall. One adverse reaction specified for Aduhelm but not for Leqembi is hypersensitivity. Hypersensitivity reactions may include angioedema (swelling of the deeper layers of the skin) and urticaria (skin rash) [15].
Leqembi vs Aduhelm: Price comparison
When it comes to medicines that aren't widely available yet, you should take any price as an indication only. Final costs tend to vary depending on your location, suppliers, or insurance coverage.
To give you an idea, a single-dose vial of Leqembi costs approximately EUR 1,043. With the recommended bi-weekly administration of the drug, this brings yearly costs for 1 person to about EUR 27,118 [16].
The indicative price of Aduhelm per single-dose vial is EUR 1,335. In terms of yearly costs for 1 person, this comes up to EUR 34,710 [17].
Where are Leqembi and Aduhelm approved?
Leqembi (lecanemab) is currently only approved in the USA and the UK, with its EMA approval expected by the end of 2024[3]. Leqembi has also submitted marketing authorization applications in China, and Japan [18, 19, 20].
Aduhelm (aducanumab) was granted accelerated approval by the FDA in the USA in June 2021. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) rejected Aduhelm's marketing application in December 2021. The application was subsequently withdrawn by Biogen in April 2022 [21]. Japan's Health Ministry has also sent a negative signal about Aduhelm's approval in the country [22].
Is Leqembi or Aduhelm not (yet) approved or available in your country? If you and your doctor are of the opinion that these treatments might benefit you, get in touch with our team of medical access experts. We can give you a personalized price quote for sourcing the medicine for you.
References:
- The anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody Lecanemab: 16 cautionary notes. Zenodo, 3 January 2023.
- Hamilton, Jon. FDA grants Alzheimer's drug Leqembi accelerated approval : Shots - Health News. NPR, 6 January 2023.
- FDA Advisory Committee Votes Unanimously to Confirm the Clinical Benefit of LEQEMBI® (lecanemab-irmb) for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Biogen | Investor Relations, 9 June 2023.
- Helmore, Edward. FDA under fire over approval of Alzheimer's drug Aduhelm. The Guardian, 29 December 2022.
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Leqembi, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Taylor, Emma. New Alzheimer's treatment, lecanemab, makes the headlines: what's next?. Alzheimer's Research UK, 13 December 2022.
- Eisai: Alzheimer's patients see Leqembi benefits even when it's halted. CNBC, 6 April 2023.
- Leqembi | ALZFORUM. Alzforum, 30 May 2023, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Aduhelm | ALZFORUM. Alzforum, 6 February 2023, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Cavazzoni, Patrizia. FDA's Decision to Approve New Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease. FDA, 7 June 2021.
- Eisai presents full results from the Clarity AD Phase III trial of lecanemab. Alzheimer Europe, 30 November 2022.
- EMERGE and ENGAGE Topline Results: Two Phase 3 Studies to Evaluate Aducanumab in Patients With Early Alzheimer's Disease. Biogen | Investor Relations, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Reference ID: 5105416. Accessdata.fda.gov, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- MEDICATION GUIDE LEQEMBI® (leh-kem'-bee) (lecanemab-irmb) injection, for intravenous use. Leqembi, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Accessdata.fda.gov, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Buy Leqembi (lecanemab-irmb) Online • Price & Costs. Everyone.org, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- Buy Aduhelm (aducanumab-avwa) Online • Price & Costs. Everyone.org, Accessed 3 August 2023.
- EISAI SUBMITS MARKETING AUTHORIZATION APPLICATION FOR LECANEMAB AS TREATMENT FOR EARLY ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE IN EUROPE | Biogen. Biogen | Investor Relations, 10 January 2023.
- Eisai Initiates BLA Submission of Data for Lecanemab in China | Biogen. Biogen | Investor Relations, 22 December 2022.
- Carvalho, Teresa, and Ray Burow. Lecanemab, for Early Alzheimer's Coming Up for Review in Japan. Alzheimer's News Today, 14 March 2022.
- Update on Regulatory Submission for Aducanumab in the European Union | Biogen. Biogen | Investor Relations, 22 April 2022.
- Swift, Rocky, et al. Eisai-Biogen Alzheimer's drug difficult to assess-Japan ministry. Reuters, 22 December 2021.