New Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatments 2022
Last updated: 13 November 2023
You can legally access new medicines, even if they are not approved in your country.
Learn howWhat is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (also called non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, NHL, or sometimes just lymphoma) is a type of cancer that starts in white blood cells known as lymphocytes. These cells are part of the body's immune system and they help the body fight infections.
NHL starts in the body’s lymph system, which is part of the immune system. They can start everywhere in the body where there is lymph tissue, including the lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, thymus and digestive organs. It starts when lymphocytes grow abnormally and form growths (tumors).
What are the symptoms of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)?
The most common symptom of nNHL is a painless swelling in a lymph node, usually in the neck, armpits or groin. Having a swollen lymph node does not mean that you have NHL, as nodes also swell when you have an infection.
Other symptoms of NHL include:
- night sweats
- unintentional weight loss
- a high temperature (fever)
- feelings of breathlessness
- persistent itching of the skin all over the body
What are the different types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)?
There are different types of NHL. It is important to know which type you have for the choice of treatment for NHL. The type of NHL depends on which type of lymphocyte is affected (B cells or T cells), how fast the cancer cells grow, and other factors.
There are over 60 subtypes of NHL, but the most common subtypes are:
- Diffuse large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Follicular lymphoma (FL)
- Small lymphocytic leukaemia/chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (SLL/CLL)
- Mantle cell lymphoma
What are the treatment options for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)?
The type of NHL treatment you need varies depending on the exact type of B or T-cell lymphoma you have, and whether it is aggressive. If your lymphoma grows slowly (indolent) and doesn't cause signs and symptoms, it does not necessarily need to be treated right away. Your doctor may recommend regular checkups to carefully monitor your condition.
If your NHL is fast-growing or causes signs and symptoms, your doctor may recommend treatment. Treatment for lymphomas includes:
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted cancer drugs
- Radiotherapy
- Stem cell transplant
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
What are the available Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) treatments?
There are several approved treatments for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL). Here are some of them:
Rylaze (asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi (recombinant)-rywn)4
Rylaze (asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi (recombinant)-rywn) is a prescription medicine that is part of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL) in adults and children aged 1 month or older who have developed hypersensitivity to E. coli-derived asparaginase.
Rylaze (asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi (recombinant)-rywn) was approved by:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA on June 30, 2021.
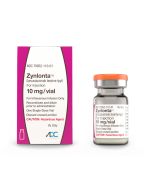
Zynlonta (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl)5,6
Zynlonta (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl) is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with certain types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that has come back (relapsed) or that did not respond to previous treatment (refractory), who have already received two or more treatments for their cancer.
Zynlonta (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl) was approved for the treatment of DLBCL in adults by:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA on April 23, 2021.
Monjuvi (tafasitamab-cxix)7
Monjuvi (tafasitamab-cxix) is a medication that is combined with lenalidomide for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Monjuvi (tafasitamab-cxix) was approved to use together with lenalidomide to treat adult patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL by:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA on July 31, 2020.
Truxima (rituximab)7
Truxima (rituximab) is a biosimilar of Rituxan (rituximab) used to treat adults with:
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) alone or with other chemotherapy medicines
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), together with the chemotherapy medicines fludarabine and cyclophosphamide
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), together with methotrexate
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) (Wegener’s Granulomatosis) and Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA), together with glucocorticoids
Truxima (rituximab) was approved by:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA on November 28, 2018, for the treatment of adult patients with NHL.
- European Medical Agency (EMA), European Union on February 16, 2018, for the treatment of patients with:
- FL stage 3 and 4
- CLL
- Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), Australia on February 16, 2018, for the treatment of patients with:
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- CLL
- Health Canada, December 11, 2019, for the treatment of patients with:
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- CLL
- Medsafe, New Zealand, August 15, 2019, for the treatment of patients with:
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
If you are trying to access Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) treatments that are approved outside of your country of residence, we might be able to help you access it with the help of your treating doctor. You can read more about the medicines we can help you access and their price below:
Rylaze (asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi (recombinant)-rywn)
Zynlonta (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl)
Monjuvi (tafasitamab-cxix)
Truxima (rituximab)
Why access and buy a new treatment for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) with everyone.org?
everyone.org is registered in The Hague with the Dutch Ministry of Health as a pharmaceutical wholesale distributor. We have helped patients from over 85 countries to access thousands of medicines including. With a prescription from your treating doctor, you can count on our expert team to safely and legally guide you to access a treatment for NHL. If you or someone you know are looking to access a medicine that is not yet approved where they live, we can support you. Contact us for more information.
References:
- Leukaemia.org.au
- Cancer.org
- NHS.uk
- Rylaze (asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi (recombinant)-rywn)
- Rylaze FDA
- Zynlonta (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl)
- Zynlonta FDA
- Monjuvi (tafasitamab-cxix)
- Monjuvi FDA
- Truxima (rituximab)
- Truxima FDA
Disclaimer: This article is not meant to influence or impact the care provided by your treating physician. Please do not make changes to your treatment without first consulting your healthcare provider. This article is not intended to diagnose or treat illness or to influence treatment options. everyone.org is as diligent as possible in compiling and updating the information on this page. However, everyone.org does not guarantee the correctness and completeness of the information provided on this page.